2011
02.02
A common question parents will ask you when they find out you work in IT is: “How do I block certain websites (mainly porn) from being accessed at home?” There are a number of ways this can be achieved, however for the typical home user who doesn’t want to run a dedicated proxy server or pay for software/a service to do this for you, the solution I like to recommend is based on DNS filtering using OpenDNS. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OpenDNS
OpenDNS web filtering will stop any machine in the house connected to your home network from being able to access porn sites as opposed to just a single machine with parental control software installed. You can select other categories you would like blocked and can also specify individual domains ie: facebook.com, but again this will block the website from being accessed on all machines connected to your home network.
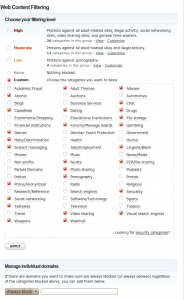
OpenDNS also offer other services as a bonus such as malware protection and anti-phising as well as detailed stats and reporting to keep you informed and updated about your network’s top internet searches allowing you to spot trends and keep an eye on your teenagers web usage.
To use OpenDNS as a content filter, simply sign up for a free account. If you do not have a static public IP address you will also need to configure your router/pc to automatically update with a DDNS client such as DynDNS which can then be configured to update your OpenDNS account by using DNS-O-Matic.
2011
02.01
VMWARE WEB ACCESS
Enable
sudo /etc/init.d/vmware-webAccess start
Disable
sudo /etc/init.d/vmware-webAccess stop
VMWARE FIREWALL
Enable
sudo /usr/sbin/esxcfg-firewall --blockIncoming
sudo /usr/sbin/esxcfg-firewall –blockOutgoing
Disable
sudo /usr/sbin/esxcfg-firewall --allowIncoming
sudo /usr/sbin/esxcfg-firewall --allowOutgoing
2011
02.01
Display a list of virtual machines on the ESXi host:
vmware-cmd -l
Start virtual server:
vmware-cmd /path/to/virtual_machine/virtual_machine.vmx start
Stop virtual server:
vmware-cmd /path/to/virtual_machine/virtual_machine.vmx stop
Check status – on or off
vmware-cmd /path/to/virtual_machine/virtual_machine.vmx getstate
2011
02.01
Copying or migrating VMWare machines from one data store to another is easily done with vCenter and the correct licensing, but if this is not available here’s how you can do so manually.
Before you can copy your VMWare machine off the ESXi host you need to allow connections through VMWare’s built in software firewall. Instructions on how to do this are detailed below:
- Select the ESXi host server you would like to manage in the vSphere client.
- Then click on the Configuration Tab > Security Profile > Properties.
- Open any relevant ports ie: SSH, NFS, SAMBA etc.
You should now be able to mount the necessary shares or simply scp the file across the network.
scp -r /vmfs/volumes/datastore/vmware_machine_X/ user@new_server:/path/to/new_home/
Once the VM has been copied or moved, you will need to import the virtual machine into the new ESXi host’s inventory.
- Click on the Configuration Tab > Storage
- Right click on the datastore where you copied the VMWare machine image to and click browse.
- Then navigate to the .vmx configuration file right click and select ‘Add to Inventory’
2011
01.31
I have been looking out for a cheap server for a while now in order to test out different high availability and failover configs, as well as a Beowulf cluster. Because the server will be hosted in my home computer lab, the two main prerequisites for the server are: Firstly, that it is as silent as possible and secondly, that it is energy efficient and uses as little power as possible.
I was lucky enough to stumble across a dual VIA EPIA-SP1300 server on ebay and snap it up for a bargain at £120. I was more than comfortable with the VIA chipset / CPUs as I am already familiar with them from a web server I host based on a previous generation chipset which has pleasantly surprised me and exceeded my expectations both in terms of speed and reliability. The two systems sit side by side in a TRAVLA C147 case which is popular among many datacenters and hosting companies as it allows you to fit 84 servers in a standard 42U rack while drawing minimal power through the mini-itx form factor.
System Specs are as follows:
2x of each
VIA EPIA-SP1300
VIA C3 @ 1.3GHz (Nehemiah core)
1GB PC3200 DDR RAM
320GB 7200rpm SATA HDD


VIA EPIA-SP1300 Operating Guide
VIA EPIA-SP1300 Manual
2011
01.30
Category:
Linux /
Tags: no tag /
WoL is a handy tool when you have servers hosted in data centers and comms rooms or stored in your loft/basement that aren’t always easily accessible to turn on and off.
To enable wol in linux follow these steps
Install ethtool:
sudo apt-get install ethtool
sudo ethtool eth0 -will tell you if your NIC compatibility
wol p|u|m|b|a|g|s|d…
Sets Wake-on-LAN options. Not all devices support this. The argument to this option is a string of characters specifying which options to enable.
p Wake on phy activity
u Wake on unicast messages
m Wake on multicast messages
b Wake on broadcast messages
a Wake on ARP
g Wake on MagicPacket(tm)
s Enable SecureOn(tm) password for MagicPacket(tm)
d Disable (wake on nothing). This option clears all previous options.
Save the following into a bash script:
#!/bin/bash
ethtool -s eth0 wol g
exit
And set to run at boot:
sudo update-rc.d [wol_script] defaults
You can then easily wake the machine by sending a magic packet to the LAN broadcast address with the server’s MAC address inside:
wakeonlan 00:11:22:aa:bb:cc
2011
01.30
From the client machine:
ssh user@server -L 5901:127.0.0.1:5900
Then launch your viewer with:
vncviewer localhost:5901
2011
01.30
Every now and again its handy to have access your servers desktop if you are running a gui. There are a number of VNC servers to choose from in linux, I like to use X11vnc. To install in Ubuntu is straight forward as always:
sudo apt-get install x11vnc
Then configure with a password:
x11vnc -storepasswd – you might want to change permission of the password file so only root can access it.
Then you can launch vnc server with the following command:
x11vnc -shared -forever -rfbauth ~/.vnc/passwd
Finally you can add the line above to a bash script and add it to run at start up if required.
2011
01.30
Proxy servers can be useful for a number of things including:
- Anonymity
- If you are at work/overseas(china) and certain websites are blocked
- If you find yourself in a public place using unsecured wifi and would like to encrypt your internet traffic
- Are abroad and would like to use regional web based services ie: BBC iPlayer
SOCKS Proxy’s are typically layer5 seeing as though they run over the session layer. To set one up just create an SSH tunnel to your home server using the following command:
ssh -D 1234 user@homeserver
All you need to do now is set your web browser to use a proxy with localhost on port 1234.
You could also setup your home ssh server as an HTTP proxy using squid if this is a more suitable option.
2011
01.30
It’s handy sometimes to be able to ssh into another server without being prompted for a password each time especially when automating scripts across a network. All you need to do is generate encryption keys for the client machine you will be using (do not use passphrase) and copy the contents of your public key to the authorized_keys file on the server:
ssh-keygen
cat .ssh/id_rsa.pub | ssh user@server "cat >> /home/user/.ssh/authorized_keys"


